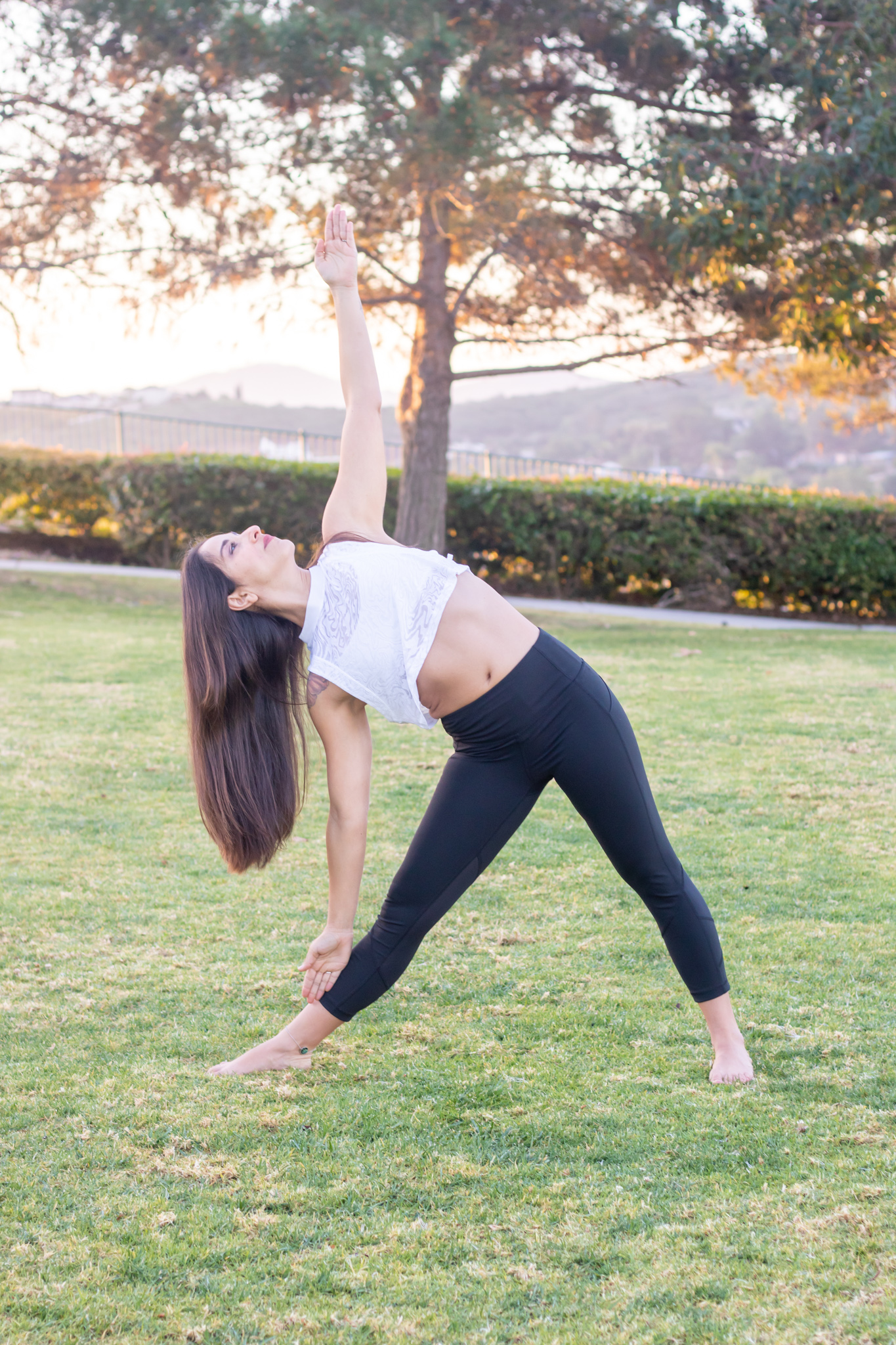
Yoga, with its holistic approach to mind-body integration, offers a myriad of benefits that extend beyond physical flexibility and strength. One of the remarkable advantages of a consistent yoga practice is its positive impact on focus and concentration. This enhancement arises from a combination of factors inherent in the practice, contributing to a sharpened mental acuity and heightened ability to concentrate. Here’s how yoga improves focus and concentration:
Mindfulness Cultivation
Yoga encourages mindfulness, the practice of being fully present in the moment. As practitioners flow through poses, focusing on breath and bodily sensations, they develop the capacity to direct their attention to the current experience. This mindfulness training naturally extends to other aspects of life, allowing individuals to engage in tasks with undivided attention.
Breath Awareness
Breath awareness is a fundamental aspect of yoga. The synchronization of breath with movement (vinyasa) in yoga postures enhances the ability to concentrate. The focus on steady, controlled breathing helps calm the mind, reducing mental distractions and allowing practitioners to stay centered in the present.
Sensory Withdrawal (Pratyahara)
Pratyahara is the withdrawal of the senses from external stimuli. Yoga practice often involves turning attention inward, limiting external distractions. This practice cultivates a heightened internal awareness, training the mind to remain focused despite potential external disturbances.
Concentration Techniques (Dharana)
Yoga incorporates concentration techniques that involve focusing on a specific point, such as a mantra, a chakra, or the breath. By consistently practicing these techniques, individuals strengthen their ability to sustain focus on a single point, a skill that directly translates to improved concentration in daily tasks.
Stress Reduction
Chronic stress can hinder focus and concentration. Yoga’s relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing and guided relaxation (shavasana), activate the parasympathetic nervous system, reducing stress hormones. As stress diminishes, mental clarity and focus naturally improve.
Enhanced Blood Flow and Oxygenation
Yoga postures often involve stretching, twisting, and inversions, which stimulate blood flow and increase oxygenation to the brain. This enhanced circulation supports cognitive function, memory, and concentration.
Neurological Impact
Yoga has been shown to influence brain plasticity and neurogenesis—the brain’s ability to form new neural connections. Certain yoga practices are associated with increased gray matter density in brain regions responsible for attention, self-awareness, and sensory processing.
Reduced Mental Chatter
Yoga promotes a sense of inner calm and mental clarity. As practitioners learn to detach from the constant stream of thoughts, mental clutter diminishes, creating a conducive environment for improved focus and concentration.
Enhanced Body-Mind Connection
Yoga’s emphasis on the mind-body connection encourages a heightened awareness of bodily sensations, movement, and alignment. This heightened awareness translates into a more focused and deliberate approach to tasks, fostering improved concentration.
Long-Term Mind Training Yoga is a holistic practice that cultivates both short-term and long-term benefits. Regular practice instills a sense of discipline and commitment, which naturally spill over into other areas of life. The dedication to a consistent yoga routine nurtures the mental stamina required for sustained focus.
Yoga’s multifaceted approach to mindfulness, breath control, sensory withdrawal, and concentration techniques creates a potent recipe for enhancing focus and concentration. By nurturing a harmonious balance between the mind and body, yoga equips practitioners with the tools to navigate the challenges of modern life with increased mental clarity, heightened concentration, and an unwavering sense of presence.