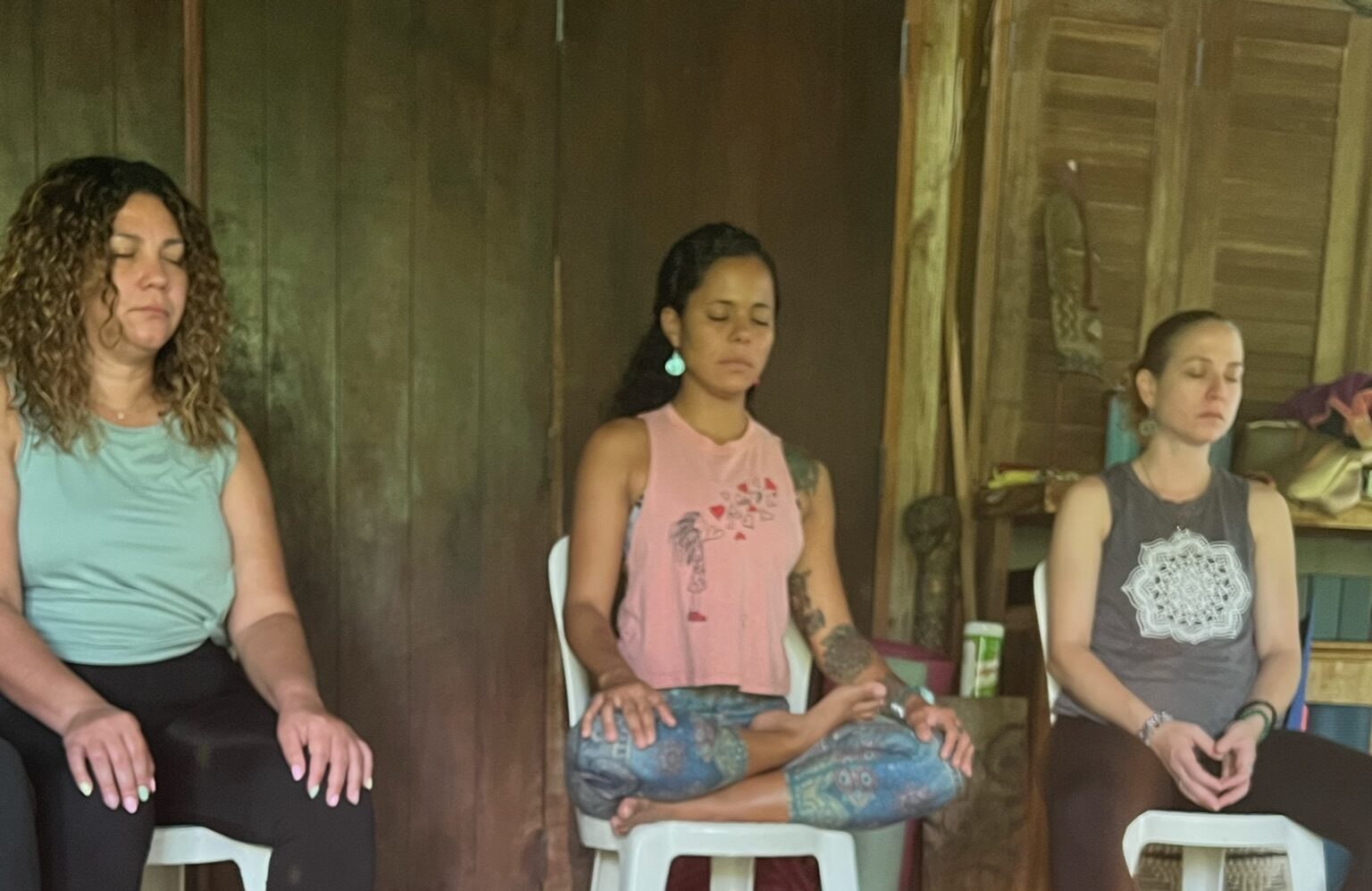
Yoga, an ancient practice rooted in Indian philosophy, has emerged as a powerful tool in the realm of mental health. Its holistic approach, which integrates physical postures, breathing techniques, and meditation, offers a multifaceted solution to various mental health challenges. The mental health benefits of yoga are increasingly recognized and validated by scientific research, making it a popular complementary practice for improving psychological well-being.
Central to yoga’s benefit for mental health is its ability to reduce stress and anxiety. The practice of yoga involves mindful movements and controlled breathing, which activate the body’s relaxation response. This shift from the sympathetic to the parasympathetic nervous system results in lower cortisol levels, the body’s stress hormone, promoting a state of calmness and relaxation. Regular yoga practice helps individuals develop a more balanced response to stress, making them less susceptible to anxiety and its related disorders.
Another key aspect of yoga’s impact on mental health is its emphasis on mindfulness. Yoga encourages present-moment awareness, allowing practitioners to observe their thoughts and feelings without judgment. This mindfulness component can lead to improved emotional regulation, reducing the intensity and frequency of negative emotions such as anger, sadness, and frustration. It fosters a heightened sense of self-awareness, enabling individuals to identify and manage mental health triggers more effectively.
Yoga also contributes to alleviating symptoms of depression. The combination of physical activity, focused breathing, and mindfulness practices in yoga can enhance mood and has been found to have antidepressant effects. Yoga stimulates the production of endorphins and other mood-enhancing neurotransmitters, promoting feelings of well-being and happiness. Furthermore, the communal aspect of group yoga classes can provide social support, reducing feelings of isolation that often accompany depression.
For those dealing with trauma and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), yoga can offer a sense of grounding and safety. Practices like trauma-informed yoga are designed to help individuals reconnect with their bodies in a safe and controlled manner, aiding in the healing process. Yoga’s focus on bodily sensations and breath control can help in managing the hyperarousal symptoms commonly experienced in PTSD.
Additionally, yoga can improve concentration and cognitive functioning. The meditative aspects of yoga enhance focus and attention, while the physical postures can increase blood flow to the brain, boosting cognitive capabilities. This aspect of yoga is particularly beneficial for those dealing with attention deficit disorders or cognitive impairments.
Yoga is a valuable practice for mental health, offering a natural and holistic way to manage stress, anxiety, depression, and other mental health issues. Its combination of physical postures, breathwork, and meditation addresses the mind-body connection, fostering overall psychological well-being. As yoga becomes more integrated into mental health care, it provides a promising complementary approach to traditional therapies, helping individuals achieve a balanced and peaceful state of mind.