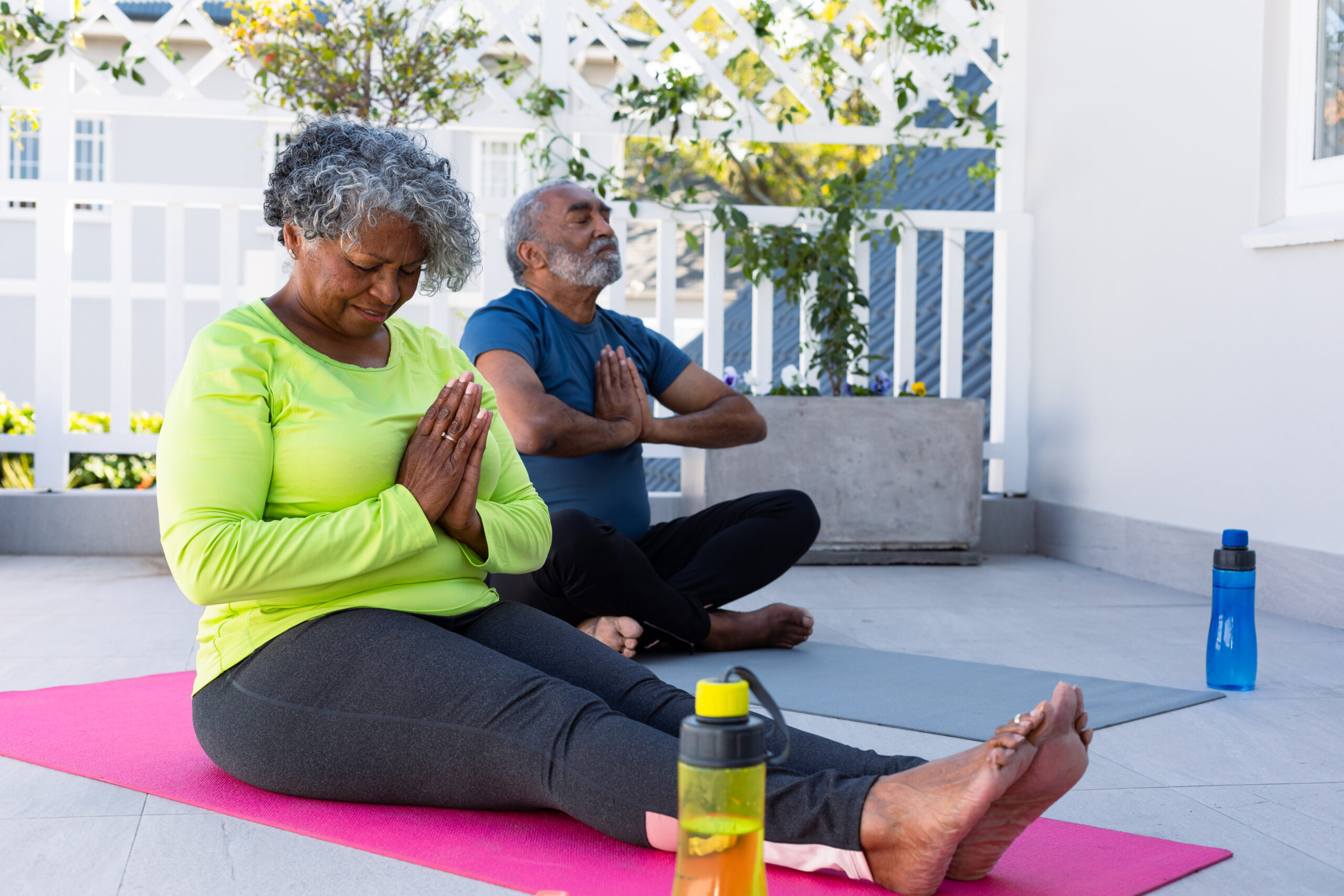
Yoga has long been revered for its physical, mental, and spiritual benefits. In recent years, scientific research has begun to illuminate how yoga can significantly influence the aging process, offering a promising approach to aging gracefully. Studies suggest that regular yoga practice can have profound effects on various aspects of aging and body systems, contributing to a healthier and more vibrant later life.
1. Enhancing Musculoskeletal Health: As the body ages, it’s common to experience a decline in muscle mass, bone density, and joint flexibility. Yoga can be a gentle yet effective way to counteract these effects. A study published in the International Journal of Yoga found that regular practice can improve balance, flexibility, and strength. Poses like Tadasana (Mountain Pose) and Vrikshasana (Tree Pose) are particularly beneficial for enhancing stability and reducing the risk of falls, a major concern in older adults.
2. Promoting Cardiovascular Health: Heart health is a critical concern as one ages. Yoga, with its combination of physical postures, breathing exercises, and meditation, has been shown to improve cardiovascular health. A study in the European Journal of Preventive Cardiology revealed that yoga can reduce high blood pressure, lower cholesterol levels, and improve circulation, all of which are vital for maintaining a healthy heart.
3. Mitigating Stress and Enhancing Mental Well-being: Aging is often accompanied by increased stress and anxiety, which can exacerbate age-related health issues. Yoga’s focus on mindfulness and breath control makes it an effective stress-reliever. Research in the Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry and Neurology indicates that yoga can reduce cortisol levels, the stress hormone, enhancing mood and overall mental well-being. Practices like Pranayama (breath control) and Dhyana (meditation) are particularly effective for calming the mind and promoting emotional balance.
4. Improving Respiratory Efficiency: As the respiratory system ages, lung capacity and oxygen efficiency may decline. Yoga’s emphasis on deep, mindful breathing can enhance respiratory function. A study in the Journal of Ayurveda and Integrative Medicine showed that practices like Kapalabhati (Skull Shining Breath) and Nadi Shodhana (Alternate Nostril Breathing) can improve lung function, oxygen uptake, and overall respiratory efficiency.
5. Supporting Cognitive Function: Cognitive decline is a significant concern in aging. However, yoga’s combination of physical movement, breathwork, and meditation can support cognitive health. Research published in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease found that yoga can enhance memory, attention, and cognitive flexibility. The meditative aspects of yoga, in particular, are believed to contribute to the preservation of brain function in older adults.
6. Enhancing Digestive Health: Digestive issues often become more prevalent with age. The gentle, twisting, and bending movements in yoga can stimulate the digestive system, promoting regularity and reducing issues like bloating and constipation. Moreover, yoga’s stress-reducing effects can mitigate stress-related digestive problems, as chronic stress is a known contributor to gastrointestinal issues.
7. Promoting Hormonal Balance: Hormonal fluctuations are a part of aging, particularly during menopause. Yoga can help in balancing hormones, reducing symptoms like hot flashes, mood swings, and insomnia. A study in Menopause, the journal of The North American Menopause Society, reported that restorative yoga can significantly alleviate menopausal symptoms, promoting a more comfortable and balanced transition during this phase.
In conclusion, yoga offers a holistic approach to aging, positively affecting various body systems and mitigating the adverse effects of aging. Its blend of physical postures, breathing techniques, and meditation provides a comprehensive, low-impact form of exercise suitable for individuals at different stages of life, including the elderly. By incorporating yoga into their routine, individuals can age with grace, maintaining vitality, mobility, and mental clarity well into their later years.